Related Document
November 2, 2024 – Vancouver, BC – Stillwater Critical Minerals Corp. (TSX.V: PGE; OTCQB: PGEZF; FSE: J0G) (the “Company” or “Stillwater”) is pleased to announce results of rhodium (“Rh”) assays conducted on core from resource expansion drilling on its 100%-owned Stillwater West platinum group element, nickel, copper, cobalt, and gold (“PGE-Ni-Cu-Co + Au”) project in Montana, USA, adjacent to Sibanye-Stillwater’s world-class critical minerals mining operations.
Highlights include:
- As shown in Table 1, widespread rhodium was returned in drill results at potentially significant co-product grades including:
- 1.13 g/t Rh in an interval that totaled 7.96 g/t Pt+Pd+Au+Rh (“4E”) over 1.2 meters in CM2023-03, starting at 308.8 meters and set within 14.6 meters of 1.38 g/t 4E including 0.118 g/t Rh; and
- 0.162 g/t Rh over 3.7 meters in CM2023-01 starting at 407.8 meters within an interval of 0.99 g/t 4E.
- Supply constraints have resulted in elevated rhodium prices since 2017. At its current two-year average price of USD 6,500/oz, and three-year year average price of USD 9,500/oz, rhodium equates to more than five times the current value of palladium or platinum.
- Results are expected to expand upon the 115,000 ounces of rhodium defined in the January 2023 Mineral Resource Estimate (“MRE”) and are similar to results from past campaigns which returned 0.103 g/t Rh over 7.9 meters in hole CM2020-05, and 0.100 g/t Rh over 6.1 meters in hole CM2007-02.
- Rhodium is mined solely as a co-product at grades that are often below 0.1 g/t. South Africa dominates global production, and there is very little mine supply in North America.
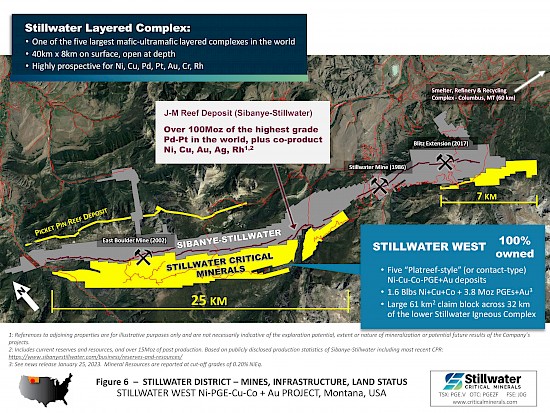
- Sibanye-Stillwater, adjacent to Stillwater’s Stillwater West project across 32 kilometers in the Stillwater Igneous Complex, is the primary US producer of Rh, mining the highest-grade PGE deposit in the world, the J-M Reef deposit.
- Recent announcements concerning lay-offs and reduced production at Sibanye-Stillwater (as a result of depressed global palladium prices) have brought bipartisan support for mining jobs in Montana and US critical mineral supply from Senators Jon Tester (D) and Steve Daines (R), both of Montana, in addition to support from other local, state, and federal officials.
- Rhodium has a high melting point, is highly corrosion resistant, and is critical in catalytic converters, along with platinum and palladium, for cleaner vehicle emissions.
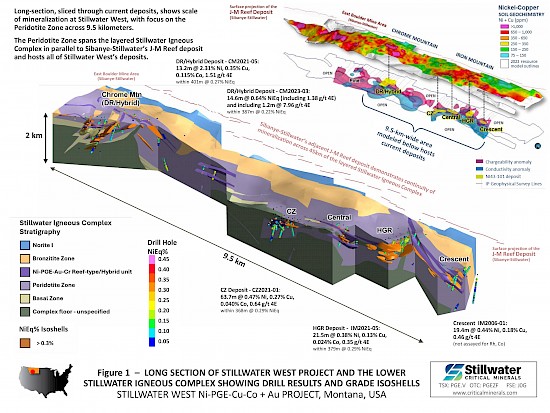
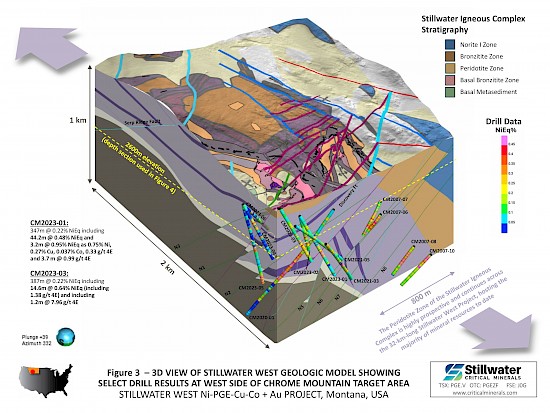
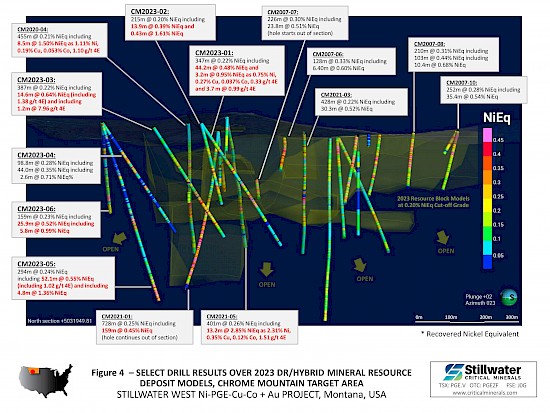
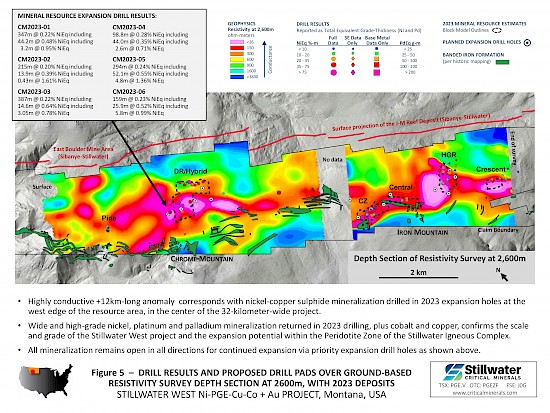
- Complete results from the expansion drill campaign, which focused on the west side of the DR and Hybrid deposits at Chrome Mountain, are being incorporated into updated block models driven by an updated 3D geologic model as announced October 16, 2024. Figure 1, updated from that release, demonstrates the impressive grade and scale of mineralization at the Stillwater West project with wide intervals at successively higher grades contained within very wide bulk-tonnage grade intervals across the 9.5-kilometer-long area that contains the current deposits, including:
- 13.2 meters of 2.31% Ni, 0.35% Cu, 0.115% Co, and 1.51 g/t 4E starting at 37.6 meters and within 400.8 meters of continuous mineralization in hole CM2021-05;
- 50.2 meters of 1.05 g/t 4E plus 0.19% Ni and other values within 728.1 meters of continuous mineralization in hole CM2021-01; and
- 44.1 meters of 0.57% Ni, 0.34% Cu, 0.045% Co, and 0.74 g/t 4E starting at 32.8 meters and within 367.6 meters of continuous mineralization in hole CZ2021-01.
- Metallurgical testing completed by AMAX confirmed recovery of rhodium along with palladium and platinum in preliminary bench-scale flotation testing at the CZ deposit area in the early 1970s.
- Past work previously reported by the Company included surface sample results of up to 5.78 g/t Rh at the HGR target in the Iron Mountain area, and 1.07 g/t Rh at Chrome Mountain in reconnaissance-scale rock sample programs (see June 11, 2020, news release).
- Early results for other rare PGEs show potential for additional value from iridium, osmium, and ruthenium which often occur along with platinum, palladium, and rhodium at Stillwater West.
Table 1 – Final results from resource expansion drilling including recent rhodium assay results.
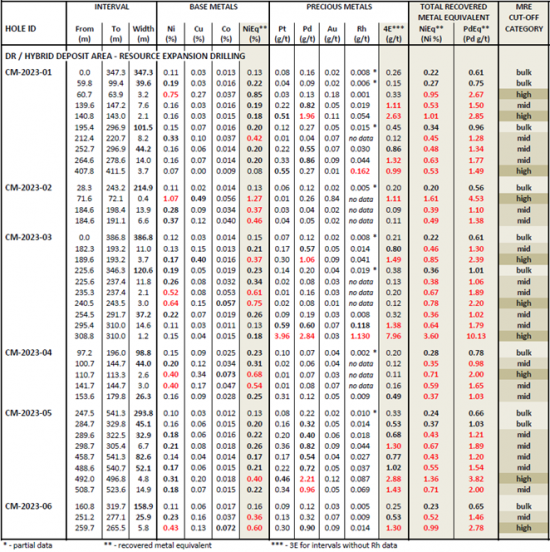
Highlighted significant intercepts with grade-thickness values over 7 percent-meter recovered NiEq are presented above, except as noted. Recovered Nickel Equivalents (“NiEq”) are presented for comparative purposes using conservative long-term metal prices (all USD): $8.00/lb nickel (Ni), $4.00/lb copper (Cu), $22.00/lb cobalt (Co), $1,000/oz platinum (Pt), $1,950/oz palladium (Pd), $1,850/oz gold (Au), and $10,000/oz rhodium (Rh). NiEq is determined as follows: NiEq% = [Ni% x recovery] + [Cu% x recovery x Cu price/ Ni price] + [Co% x recovery x Co price / Ni price] + [Pt g/t x recovery / 31.103 x Pt price / Ni price / 2,204 x 100] + [Pd g/t x recovery / 31.103 x Pd price / Ni price / 2,204 x 100] + [Au g/t x recovery / 31.103 x Au price / Ni price / 2,204 x 100]. In the above calculations: 31.103 = grams per troy ounce, 2,204 = lbs per metric tonne, and 100 and 0.01 convert assay results reported in % and g/t. The following recoveries have been assumed for purposes of the above equivalent calculations: 85% for Ni and 90% for all other listed metals, based on recoveries at similar nearby operations. Total metal equivalent values include both base and precious metals. In terms of dollar value, 0.20% nickel equates to a copper value of 0.40%, or a palladium value of 0.48 g/t, using the above metal values. Intervals are reported as drilled widths and are believed to be representative of the actual width of mineralization.
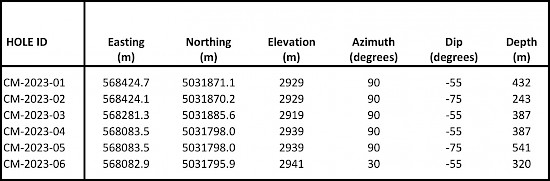
Table 2 – Drill Hole Location and Depths
Michael Rowley, President and CEO, commented, “The strength and sheer scale of mineralization at Stillwater West continues to impress us as we add mineralization at several grade cut-offs, providing us with excellent optionality on potential mine methods as we advance towards our vision of becoming a primary source of critical minerals in the US. The polymetallic nature of our deposits is also strongly in our favor as the longest lived and most profitable mines in the world are almost without exception large and polymetallic. Anglo American’s Mogalakwena mines and Ivanhoe’s Platreef mine – our geologic parallels in South Africa’s Bushveld Complex - are excellent examples of large-scale polymetallic critical minerals mines in similar geology. Armed with these drill results and our new understanding of the layered geology of the Stillwater Complex per our updated 3D geologic model as announced recently, we now have the components necessary to update our current resource estimate. We look forward to further announcements from our flagship asset in addition to updates from our non-core assets.”
Dr. Danie Grobler, Vice-President of Exploration, commented, “The wealth of exploration drilling and assay data available on the Stillwater West project area greatly advanced our understanding of the mineralization controls and detailed geological interpretation. Recent drill results further support our geological models and understanding of mineralization controls within the main target areas. The current models now confirm continuity of the mineralized zones and their correlation with the A and B Chromitite horizons within the lower part of the Peridotite Zone. Both these chromite-rich horizons, viewed as thick stratiform ‘reef’- type horizons, are PGE-enriched and particularly rich in rhodium. More importantly, the reported high-grade rhodium results have now been confirmed to correlate with these two specific chromitite units and correspond to geochemical and geophysical anomalies associated with our existing resource areas defined during 2023. This largely confirms our understanding of their occurrence, and our ability to effectively target extensions and new areas”.
Recent Events in Global Platinum Group Elements Markets, Including US Government Support
In September 2024, Sibanye-Stillwater announced a substantial reduction in operations at the mines beside Stillwater West, primarily as a result of low global palladium prices. The response from the community and also local, state and federal governments was swift and supportive, with Senators Tester and Daines for example announcing bipartisan support for Montana mining jobs and US critical mineral production to bolster domestic supplies and counter foreign dumping with the intent to drive prices down. These actions were focused on palladium but similar comments and lobby efforts have been applied to nickel, cobalt, and other critical minerals in recent years, as a result of a flood of cheaper metal from Russia and Chinese-funded operations in Indonesia, the DRC, and other locations.
In October 2024, the US government approached the G-7 nations with a proposal for sanctions on Russian palladium in a further demonstration of the US’ desire to counter foreign supplies and allow its domestic resources to advance.
Most recently, Sibanye-Stillwater celebrated the publication of the final regulations for Section 45X of the Inflation Reduction Act from the US Department of the Treasury which clarified important points that will likely result in significant tax credits for production of critical minerals from their US operations.
The importance of having proactive and supportive government cannot be understated as the US looks to expand its supply chains of critical minerals.
The Company has been working with the US Geological Survey for over six years, is the industry partner on Department of Energy grants totaling USD 2.75M to date, and is actively pursuing additional government funding for critical mineral supply.
Figure 2 – Stillwater Critical Minerals President and CEO Michael Rowley with Federal politicians from Montana in May 2024 at the Hart Senate Office Building, Washington, DC. From L-R: Senator Jon Tester (D), Representative Matt Rosendale (R), Michael Rowley, Representative Ryan Zinke (R), and Senator Steve Daines (R).

Upcoming Events
Stillwater’s President and CEO, Michael Rowley, will be available for meetings and presenting at the following events:
- Precious Metals Summit – Zurich, CH, November 11-12, 2024. For more information, click here.
- 121 Mining Events – London, UK, November 14-15. For more information, click here.
About Stillwater Critical Minerals Corp.
Stillwater Critical Minerals (TSX.V: PGE | OTCQB: PGEZF | FSE: J0G) is a mineral exploration company focused on its flagship Stillwater West Ni-PGE-Cu-Co + Au project in the iconic and famously productive Stillwater mining district in Montana, USA. With the addition of two renowned Bushveld and Platreef geologists to the team and strategic investments by Glencore plc, the Company is well positioned to advance the next phase of large-scale critical mineral supply from this world-class American district, building on past production of nickel, copper, and chromium, and the on-going production of platinum group, nickel, and other metals by neighboring Sibanye-Stillwater. An expanded NI 43-101 mineral resource estimate, released January 2023, positions Stillwater West with the largest nickel resource in an active US mining district as part of a compelling suite of nine minerals now listed as critical in the USA.
Stillwater also holds the high-grade Drayton-Black Lake- gold project adjacent to Nexgold Mining’s development-stage Goliath Gold Complex in northwest Ontario, currently under an earn-in agreement with Heritage Mining, and the Kluane PGE-Ni-Cu-Co critical minerals project on trend with Nickel Creek Platinum‘s Wellgreen deposit in Canada‘s Yukon Territory. The Company also holds the Duke Island Cu-Ni-PGE property in Alaska, now subject to an LOI towards an earn-in agreement with Granite Creek Copper, and maintains a back-in right on the high-grade past-producing Yankee-Dundee in BC, following its sale in 2013.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION, PLEASE CONTACT:
Michael Rowley, President, CEO & Director – Stillwater Critical Minerals
Email: info@criticalminerals.com Phone: (604) 357 4790
Web: http://criticalminerals.com Toll Free: (888) 432 0075
Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2023 drill core samples were analyzed by ACT Labs in Vancouver, B.C. Sample preparation: crush (< 7 kg) up to 80% passing 2 mm, riffle split (250 g) and pulverize (mild steel) to 95% passing 105 µm included cleaner sand. Gold, platinum, and palladium were analyzed by fire assay (1C-OES) with ICP finish. Selected major and trace elements were analyzed by peroxide fusion with 8-Peroxide ICP-OES finish to insure complete dissolution of resistate minerals. Following industry QA/QC standards, blanks, duplicate samples, and certified standards were also assayed.
Mr. Mike Ostenson, P.Geo., Managing Geologist at Stillwater, is the qualified person for the purposes of National Instrument 43-101, and he has reviewed and approved the technical disclosure contained in this news release.
Forward-Looking Statements
This news release includes certain statements that may be deemed “forward-looking statements”. All statements in this release, other than statements of historical facts including, without limitation, statements regarding potential mineralization, historic production, estimation of mineral resources, the realization of mineral resource estimates, interpretation of prior exploration and potential exploration results, the timing and success of exploration activities generally, the timing and results of future resource estimates, permitting time lines, metal prices and currency exchange rates, availability of capital, government regulation of exploration operations, environmental risks, reclamation, title, and future plans and objectives of the company are forward-looking statements that involve various risks and uncertainties. Although Stillwater Critical Minerals believes the expectations expressed in such forward-looking statements are based on reasonable assumptions, such statements are not guarantees of future performance and actual results or developments may differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are based on a number of material factors and assumptions. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those in forward-looking statements include failure to obtain necessary approvals, unsuccessful exploration results, changes in project parameters as plans continue to be refined, results of future resource estimates, future metal prices, availability of capital and financing on acceptable terms, general economic, market or business conditions, risks associated with regulatory changes, defects in title, availability of personnel, materials and equipment on a timely basis, accidents or equipment breakdowns, uninsured risks, delays in receiving government approvals, unanticipated environmental impacts on operations and costs to remedy same, and other exploration or other risks detailed herein and from time to time in the filings made by the companies with securities regulators. Readers are cautioned that mineral resources that are not mineral reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability. Mineral exploration and development of mines is an inherently risky business. Accordingly, the actual events may differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. For more information on Stillwater Critical Minerals and the risks and challenges of their businesses, investors should review their annual filings that are available at www.sedar.com.
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.