Related Document
January 10, 2023 – Vancouver, BC – Stillwater Critical Minerals (formerly Group Ten Metals) (TSX.V: PGE; OTCQB: PGEZF; FSE: 5D32) (the “Company” or “SWCM”) is pleased to announce the first tranche of results from work completed in 2022 on its 100%-owned Stillwater West platinum group element, nickel, copper, cobalt, and gold (“PGE-Ni-Cu-Co + Au”) project adjacent to Sibanye-Stillwater’s mining operations in Montana, USA.
A series of news releases are planned to report the results of work on key objectives including expansion of the 2021 Mineral Resource Estimate (the “2021 MRE”), integration of Platreef geologic models, and field campaigns including geophysical and geological field programs both within and outside defined deposit areas. Additional updates are also expected from on-going carbon sequestration testing and other initiatives the Company is currently advancing.
Pine Target Highlights
- Rock chip samples taken across approximately two meters of exposed shear in a trench at the Pine target in 2022 returned high-grade gold, palladium and platinum mineralization with an average of 9.0 g/t Au, 0.69 g/t Pd, and 0.69 g/t Pt (see Table 1). Significant nickel and cobalt values are also reported, consistent with past results from this area.
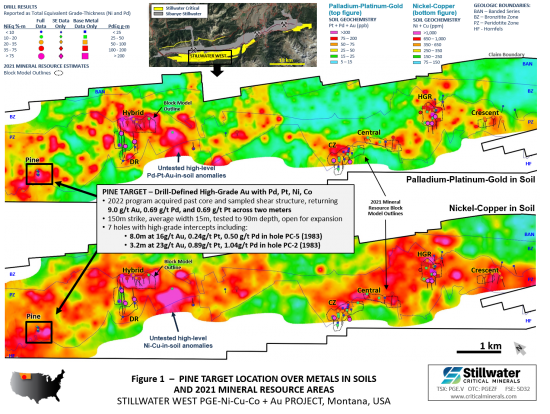
- Work in 2022 also included the acquisition of historic core to support the advancement of drill-defined high-grade mineralization at Pine towards completion of an NI-43-101-compliant resource. Mineralization at Pine was not included in the five deposits delineated by the 2021 MRE at the Chrome and Iron Mountain target areas, up to nine kilometers east of Pine within the Stillwater Igneous Complex.
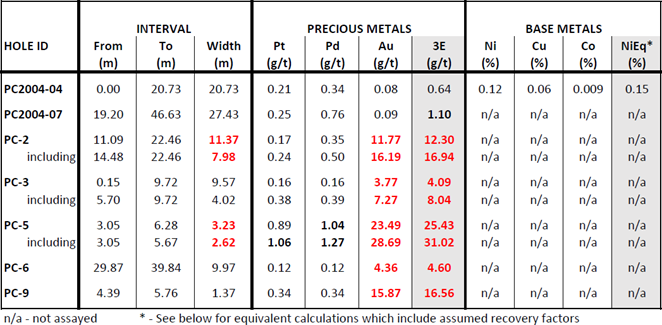
- Historic drilling at Pine returned values of 16.94 g/t 3E (16.19 g/t Au, 0.24 g/t Pt, 0.50 g/t Pd) over 7.98 meters and 31.02 g/t 3E (28.7 g/t Au, 1.06 g/t Pt, 1.27 g/t Pd) over 2.6 meters in the area of the 2022 trench samples (see Table 2, Figure 1, and news releases on June 4, 2019, and January 25, 2019).
- Mineralization remains open to expansion in all directions including towards very high-level gold-in-soil anomalies extending up to two kilometers west of Pine, in addition to the adjacent high-level palladium, platinum, and nickel-copper soil anomalies shown in Figure 1.
- Elevated gold values are also demonstrated in high-grade drill results two kilometers east of Pine at the Chrome Mountain deposit area (see May 3, 2022, news release reporting 13.2 meters of 2.31% Ni, 0.82 g/t Au, 0.43 g/t Pd, 0.25 g/t Pt, 0.35% Cu and 0.115% Co), and nine kilometers east at the Iron Mountain deposit area (see May 29, 2020, news release announcing identification of a “gold suite” of pathfinder elements that co-occur in high-grade samples).
Table 1 – Assay results from 2022 trench samples at the Pine Target, Stillwater West project
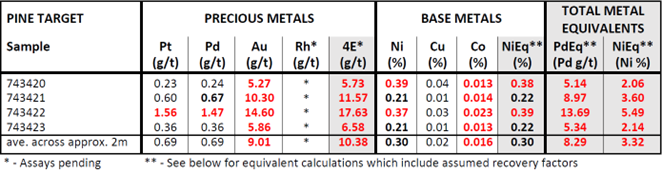
Table 2 – Highlight mineralized drill intercepts from the Pine Target, Stillwater West project
Notes to reported values:
- Ni and Pd equivalents are presented for comparative purposes using conservative long-term metal prices (all USD): $8.00/lb nickel (Ni), $4.00/lb copper (Cu), $24.00/lb cobalt (Co), $1,000/oz platinum (Pt), $2,200/oz palladium (Pd), and $1,800/oz gold (Au).
- Nickel Equivalent in Table 1 is determined as follows: NiEq% = [Ni% x recovery] + [Cu% x recovery x Cu price/ Ni price] + [Co% x recovery x Co price / Ni price] + [Pt g/t x recovery / 31.103 x Pt price / Ni price / 2,204 x 100] + [Pd g/t x recovery / 31.103 x Pd price / Ni price / 2,204 x 100] + [Au g/t x recovery / 31.103 x Au price / Ni price / 2,204 x 100]
- Nickel Equivalent in Table 2 is determined as follows: NiEq% = [Ni% x recovery] + [Cu% x recovery x Cu price / Ni price] + [Co% x recovery x Co price / Ni price]
- Palladium Equivalent is determined as follows: PdEq g/t = NiEq x 0.401
- In the above calculations: 31.103 = grams per troy ounce, 2,204 = lbs per metric tonne, and 100 and 0.01 convert assay results reported in % and g/t.
- The following recoveries have been assumed for purposes of the above equivalent calculations: 85% for Ni and 90% for all other listed metals, based on recoveries at similar nearby operations.
- Intervals are reported as drilled widths and are not believed to be representative of the true width of mineralization.
Dr. Danie Grobler, Vice-President of Exploration for SWCM, commented, “The Pine samples display an anomalous suite of shear zone hosted mineralization with elevated Au, Ni, Co and PGEs. These shear zones appear to trend in an NNW direction, forming an exciting and important target for advancement. The host rock is intensely sheared and altered Bronzite Cumulate with disseminated to massive chromite and possibly formed the focus for a cross-cutting post-magmatic hydrothermal alteration event. Recently identified precious and base metal in soil anomalies at the Gold Ridge and Pegmatoid Ridge targets to the west of Pine are coincident with large, intense anomalies in geophysical surveys and have not been explored in the past.”
Michael Rowley, President and CEO, commented, “Our expanding understanding of high-grade gold and platinum group element mineralization, alongside the wealth of critical minerals that the Stillwater district is known for, highlights the surprisingly underexplored nature of the lower Stillwater Igneous Complex and the potential that exists for the advancement of multiple world-class ore bodies across the 32-kilometer span of the Stillwater West project. We look forward to additional reports on recent work including our updated mineral resource estimate as those results become available, and beyond that to announcing our 2023 plans for continued expansion in this iconic American district.”
About the Pine Target
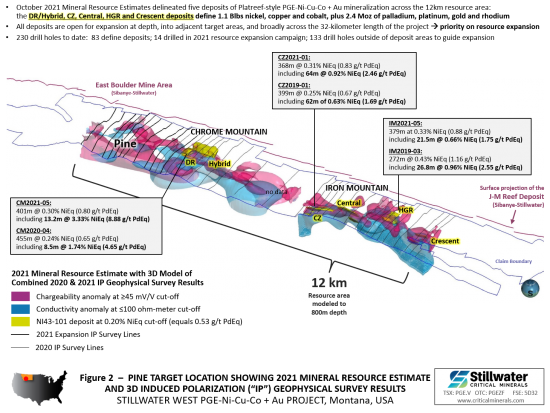
The Pine target is situated in the Wild West target area, approximately two kilometers west of deposits at the Chrome Mountain area, and nine kilometers west of deposits at the Iron Mountain area (see Figures 1 and 2). It is on the western side of the 12-kilometer-long resource area that contains the five deposits modeled in the 2021 MRE and has been detailed by Induced Polarization (IP) geophysical surveys conducted by the Company in 2020 and 2021. As shown in Figure 2, the broader Pine target area is characterized by an intense multi-kilometer-scale IP geophysical signature.
Results to date demonstrate very high-grade gold, palladium and platinum mineralization in drilling, soils and rock sampling, in addition to significant battery metals - in particular nickel and cobalt.
Work in 2022 focused on a geological sampling and mapping program, and the acquisition of some of the drill core from the 1983 and 2004 drill campaigns with the objective of finalizing drill targets and advancing drill-defined high-grade gold with PGE-Ni-Cu mineralization towards completion of an NI43-101-compliant mineral resource. At present, seven drill holes from 1983 and 2004 define a precious metals-rich mineralized zone that is 150 meters strike with an average width of 15 meters that has been tested to a depth of 90 meters (see Table 2 and news releases from June 4, 2019, January 25, 2019, and May 13, 2020). Mineralization remains open to expansion in all directions including towards very high-level gold-in-soil anomalies extending up to two kilometers west of Pine, in addition to the adjacent high-level palladium, platinum, and nickel-copper soil anomalies.
High-grade gold plus platinum group elements values have also been reported from drilling and surface samples at the Chrome and Iron Mountain deposit areas in addition to large-scale nickel, copper and cobalt bulk tonnage mineralization.
Pine is one of several priority targets for follow up exploration in 2023.
Mineral Resource Update and Integration of Platreef Geologic Models
The update to the 2021 MRE is entering the final stages of completion with release anticipated early in 2023. The updated models are driven by the integration of geologic models from the Platreef district of South Africa’s Bushveld complex, and the most recent 14-hole expansion drill campaign which returned multiple wide and high-grade battery and precious metal intercepts in wide step-outs from known mineralization at the three most advanced deposit areas within the 12-kilometer core of the project.
Significance of the Platreef Deposit Model
The Stillwater Igneous Complex is well-known to parallel South Africa’s Bushveld Igneous Complex, and developments at the Stillwater complex have generally paralleled those at the Bushveld, highlighting their significant geologic similarities. For example, Sibanye-Stillwater’s high-grade J-M Reef deposit was discovered by the direct application of geologic models developed during discovery of the high-grade Merensky reef deposit in the Bushveld.
More recent developments on the Bushveld have focused on the Platreef deposits, in the northern limb of the Bushveld, which depart from the conventional narrow reef-type mines that dominate global platinum group element mining with the occurrence of thick mineralized horizons that support bulk mining techniques and include much higher battery metal content. The mines of the Platreef are among the largest and most profitable in the world, and their mix of commodities offers an attractive internally hedged suite of in-demand critical minerals that is globally very rare. Starting with Anglo American’s PGE-Ni-Cu Mogalakwena mines in 1993 and continuing today with Ivanhoe’s underground Platreef mine, these mines have demonstrated the world-class nature of these bulk-tonnage, critical mineral systems within the Bushveld complex.
Platreef-style deposits also compare very favorably in an environmental sense as they contain nickel sulphide mineralization that is capable of producing nickel metal with a much smaller footprint than nickel recovered from laterite deposits, which currently represents the majority of global nickel supply. Additional environmental benefits are possible through reaction of atmospheric carbon dioxide with certain ultramafic rocks present in Platreef-style deposits. Testwork is underway to evaluate the potential for commercial-scale carbon sequestration during a possible mining operation Stillwater West.
About Stillwater West
Stillwater Critical Minerals is rapidly advancing the Stillwater West PGE-Ni-Cu-Co + Au project towards becoming a world-class source of low-carbon, sulphide-hosted nickel, copper, and cobalt, critical to the electrification movement, as well as key catalytic metals including platinum, palladium and rhodium used in catalytic converters, fuel cells, and the production of green hydrogen. Stillwater West positions SWCM as the second-largest landholder in the Stillwater Complex, with a 100%-owned position adjoining and adjacent to Sibanye-Stillwater’s PGE mines in south-central Montana, USA1. The Stillwater Complex is recognized as one of the top regions in the world for PGE-Ni-Cu-Co mineralization, alongside the Bushveld Complex and Great Dyke in southern Africa, which are similar layered intrusions. The J-M Reef, and other PGE-enriched sulphide horizons in the Stillwater Complex, share many similarities with the highly prolific Merensky and UG2 Reefs in the Bushveld Complex. SWCM’s work in the lower Stillwater Complex has demonstrated the presence of large-scale disseminated and high-sulphide battery metals and PGE mineralization, similar to the Platreef in the Bushveld Complex2. Drill campaigns by the Company, complemented by a substantial historic drill database, have delineated five deposits of Platreef-style mineralization across a core 12-kilometer span of the project, all of which are open for expansion into adjacent targets. Multiple earlier-stage Platreef-style and reef-type targets are also being advanced across the remainder of the 32-kilometer length of the project based on strong correlations seen in soil and rock geochemistry, geophysical surveys, geologic mapping, and drilling.
About Stillwater Critical Minerals Corp.
Stillwater Critical Minerals (TSX.V: PGE | OTCQB: PGEZF) is a mineral exploration company focused on its flagship Stillwater West PGE-Ni-Cu-Co + Au project in the iconic and famously productive Stillwater mining district in Montana, USA. With the recent addition of two renowned Bushveld and Platreef geologists to the team, the Company is well positioned to advance the next phase of large-scale critical mineral supply from this world-class American district, building on past production of nickel, copper, and chromium, and the on-going production of platinum group and other metals by neighboring Sibanye-Stillwater. The Platreef-style nickel and copper sulphide deposits at Stillwater West contain a compelling suite of critical minerals and are open for expansion along trend and at depth, with an updated NI 43-101 mineral resource update expected early in 2023.
Stillwater Critical Minerals also holds the high-grade Black Lake-Drayton Gold project adjacent to Treasury Metals’ development-stage Goliath Gold Complex in northwest Ontario, which is currently under an earn-in agreement with an option to joint venture whereby Heritage Mining may earn up to a 90% interest in the project by completing payments and work on the project. The Company also holds the Kluane PGE-Ni-Cu-Co critical minerals project on trend with Nickel Creek Platinum‘s Wellgreen deposit in Canada‘s Yukon Territory.
About the Metallic Group of Companies
The Metallic Group is a collaboration of leading precious and base metals exploration companies, with a portfolio of large, brownfield assets in established mining districts adjacent to some of the industry’s highest-grade producers of silver and gold, platinum and palladium, and copper. Member companies include Metallic Minerals in the Yukon’s high-grade Keno Hill silver district and La Plata silver-gold-copper district of Colorado, Granite Creek Copper in the Yukon’s high-grade Minto copper district, and Stillwater Critical Minerals in the Stillwater PGM-nickel-copper district of Montana. The founders and team members of the Metallic Group include highly successful explorationists formerly with some of the industry’s leading explorers/developers and major producers. With this expertise, the companies are undertaking a systematic approach to exploration using new models and technologies to facilitate discoveries in these proven, but under-explored, mining districts. The Metallic Group is headquartered in Vancouver, BC, Canada, and its member companies are listed on the Toronto Venture, US OTC, and Frankfurt stock exchanges.
Note 1: References to adjoining properties are for illustrative purposes only and are not necessarily indicative of the exploration potential, extent or nature of mineralization or potential future results of the Company’s projects.
Note 2: Magmatic Ore Deposits in Layered Intrusions—Descriptive Model for Reef-Type PGE and Contact-Type Cu-Ni-PGE Deposits, Michael Zientek, USGS Open-File Report 2012–1010.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION, PLEASE CONTACT:
Michael Rowley, President, CEO & Director
Email: info@criticalminerals.com Phone: (604) 357 4790
Web: http://criticalminerals.com Toll Free: (888) 432 0075
Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2022 rock chip samples were analyzed by ACT Labs in Vancouver, B.C. Sample preparation: crush (< 7 kg) up to 80% passing 2 mm, riffle split (250 g) and pulverize (mild steel) to 95% passing 105 µm included cleaner sand. Gold, platinum, and palladium were analyzed by fire assay (1C-OES) with ICP finish. Selected major and trace elements were analyzed by peroxide fusion with 8-Peroxide ICP-OES finish to insure complete dissolution of resistate minerals. Following industry QA/QC standards, blanks, duplicate samples, and certified standards were also assayed.
2004 drilling was conducted by SWCM’s QP while working for Premium Exploration. 1983 drill results are considered historic and have not been independently verified by SWCM.
1980s assay data was obtained from a 1986 report by geologist R.J. Warchola titled “A Hydrothermal Gold Occurrence on Chrome Mountain, Stillwater Complex, Montana” published in the Montana Geologic Society and Yellowstone Bighorn Research Association Joint Field Conference and Symposium: Geology of the Beartooth Uplift and Adjacent Basin: YBRA 50th Anniversary Edition, 1986; and a 1984 internal report by R.J. Warchola titled “Geologic Report on the Pine Claim, Sweetgrass County, Montana February 1984”
Mr. Mike Ostenson, P.Geo., is the qualified person for the purposes of National Instrument 43-101, and he has reviewed and approved the technical disclosure contained in this news release.
Forward-Looking Statements
Forward Looking Statements: This news release includes certain statements that may be deemed “forward-looking statements”. All statements in this release, other than statements of historical facts including, without limitation, statements regarding potential mineralization, historic production, estimation of mineral resources, the realization of mineral resource estimates, interpretation of prior exploration and potential exploration results, the timing and success of exploration activities generally, the timing and results of future resource estimates, permitting time lines, metal prices and currency exchange rates, availability of capital, government regulation of exploration operations, environmental risks, reclamation, title, and future plans and objectives of the company are forward-looking statements that involve various risks and uncertainties. Although Stillwater Critical Minerals believes the expectations expressed in such forward-looking statements are based on reasonable assumptions, such statements are not guarantees of future performance and actual results or developments may differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are based on a number of material factors and assumptions. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those in forward-looking statements include failure to obtain necessary approvals, unsuccessful exploration results, changes in project parameters as plans continue to be refined, results of future resource estimates, future metal prices, availability of capital and financing on acceptable terms, general economic, market or business conditions, risks associated with regulatory changes, defects in title, availability of personnel, materials and equipment on a timely basis, accidents or equipment breakdowns, uninsured risks, delays in receiving government approvals, unanticipated environmental impacts on operations and costs to remedy same, and other exploration or other risks detailed herein and from time to time in the filings made by the companies with securities regulators. Readers are cautioned that mineral resources that are not mineral reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability. Mineral exploration and development of mines is an inherently risky business. Accordingly, the actual events may differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. For more information on Stillwater Critical Minerals and the risks and challenges of their businesses, investors should review their annual filings that are available at www.sedar.com.
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.